Welcome to the GSFC Exoplanet Modeling and Analysis Center (EMAC)
EMAC serves as a catalog, repository and integration platform for modeling and analysis resources focused on the study of exoplanet characteristics and environments. EMAC is a key project of the GSFC Sellers Exoplanet Environments Collaboration (SEEC).
If you've used EMAC in any part of your research, please cite our RNAAS paper either in your methods section or in the "Software used" portion of any manuscripts; see the FAQ for more information.
More Information on EMAC for first-time visitors...
If you make use of tools linked or hosted on EMAC: please use the following statement in your publication acknowledgements: “This research made use of the NASA Exoplanet Modeling and Analysis Center (EMAC), which is funded by the NASA Planetary Science Division's Internal Scientist Funding Model.”
Stay up to date with EMAC!
- Subscribe to our monthly RSS messages on new updates and tools.
- Check out the Bluesky account @exoplanetmodels.bsky.social (not an official NASA account), where new tools and features are highlighted.
Help us improve EMAC!
-
Email us with general feedback at
and tell us what you'd change or improve.
- Click the
 icon in a resource box to provide suggestions for an individual tool or tools.
icon in a resource box to provide suggestions for an individual tool or tools.
Other EMAC info!
- EMAC is intended as a clearinghouse for the whole research community interested in exoplanets, where any software or model developer can submit their tool/model or their model output as a contribution for others to use.
- EMAC provides a searchable and sortable database for available source code and data output files - both resources hosted locally by EMAC as well as existing external tools and repositories hosted elsewhere.
- The EMAC team also helps develop new web interfaces for tools that can be run “on-demand” or model grids that can be interpolated for more individualized results.
- If you would like to submit a new tool/model to EMAC, please visit our Submit a Resource page.
- For help with tutorials for select resources/tools use the “Demo” buttons below and subscribe to our YouTube channel.
- Watch this video for a walk-through of the whole EMAC site, including how to submit a new tool and how to access information for each resource.
EMAC co-leads are Joe P. Renaud and Eric Lopez; more information on EMAC staffing and organization can be found on Our Team page.
EMAC has launched a new community-supported curator program, and we need your help! Check out our
curator page to learn how exoplanet experts like yourself can support EMAC's mission, and help us spread the word about this new initiative!
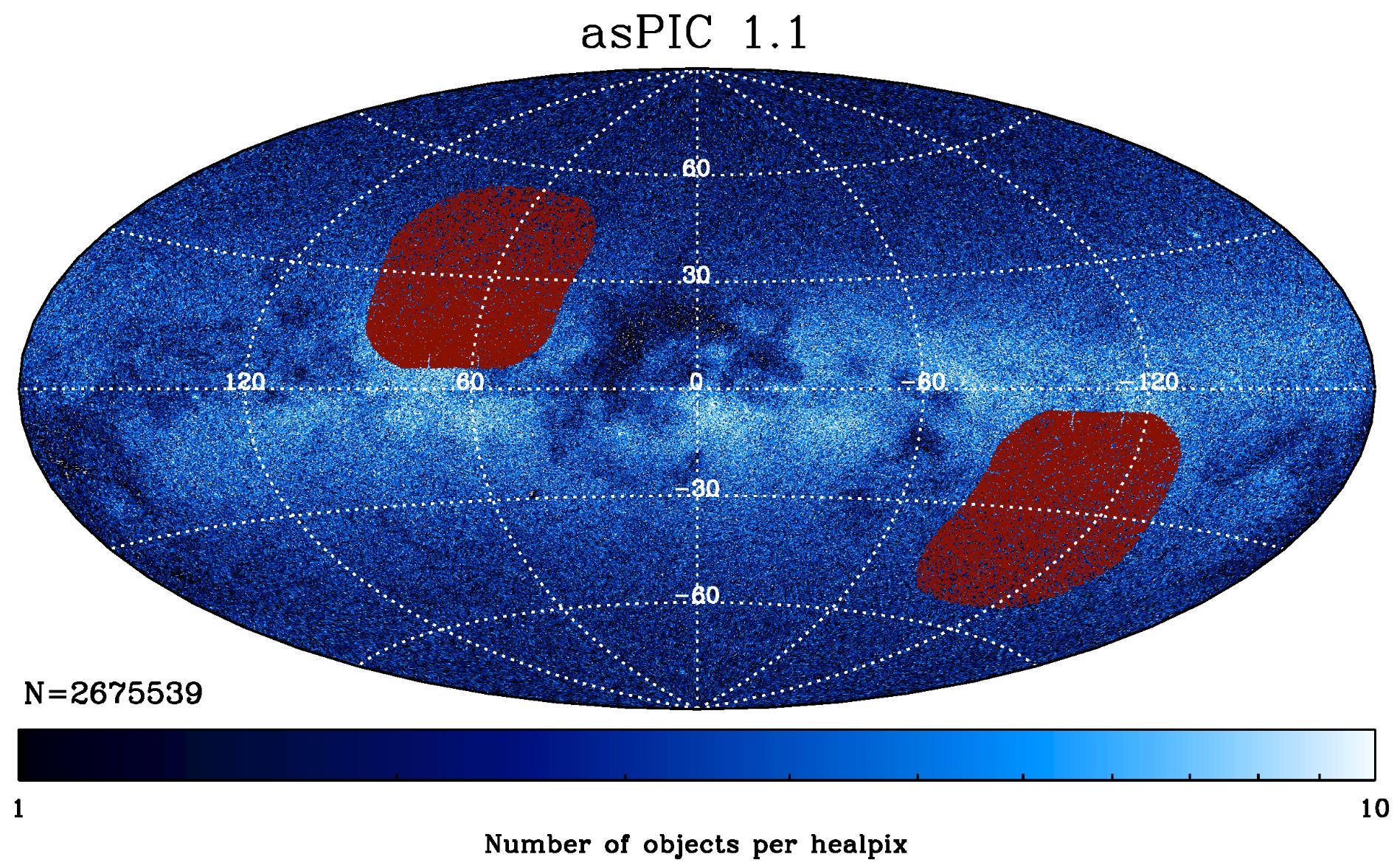
The Habitable Worlds Observatory Preliminary Input Catalog (HPIC) is a list of ~13,000 nearby bright stars that will be potential targets for the Habitable Worlds Observatory in its search for Earth-sized planets around Sun-like stars. It was constructed using the TESS and Gaia DR3 catalogs, and uses an automated pipeline to compile stellar measurements and derived astrophysical properties for all stars.
Version 1.1 adds modeled UV fluxes for all objects.
Code Language(s):
Last updated: Mar. 24, 2025
Version: 1.1
Subcategories:
Stellar Parameter Fitting
Imaging Survey Predictions
Host Star Catalogs
HZ_evolution is a Python package to characterize the habitable histories of exoplanets. Given inputs of a planet's current effective flux and host star properties, HZ_evolution calculates its instellation history, the evolution of the star's Habitable Zone, and the duration the planet spends inside or outside the Habitable Zone.
Code Language(s): Python
Last updated: Feb. 18, 2025
Version: v1.0.0
Subcategories:
Model-Fitting Tools
Population Simulations and Catalogs
The TRAPPIST Habitable Atmosphere Intercomparison (THAI) project is a model inter-comparison effort between four GCMs: ExoCAM, LMD-G, ROCKE3D and the UM – examining a single interesting test case (TRAPPIST-1e) under several different atmosphere scenarios. The CKAN data repository provides NetCDF files for each case, allowing for examination and intercomparison of results from the different models. Scripts to process the data and plot them are available on our Github repository.
Code Language(s): N/A
Last updated: Sep. 22, 2022
Version: 1
Subcategories:
2D/3D Atm Models
Transit/Eclipse RT
Visualization of the open data from the NASA Exoplanets Archive of planets outside the solar system that are similar to the Earth and habitable.
By means of NASA API exoplanets were parsed and stored to SQLite database: "content.sqlite".
There are two visualizations of the parsed data:
- Python 3 file "khistogram.py" samples data into "khistogram.js" which is used by "khistogram.htm" to visualize data with D3.js library;
- Python 3 file"kbchart.py" samples data into "kbchart.js" which is used by "kbchart.htm" to visualize data with Google BubbleChart.
Code Language(s): HTML, JavaScript, Python3
Last updated: Apr. 13, 2021
Subcategories:
Data Visualization Tools
The ESA PLAnetary Transits and Oscillations of stars (PLATO) mission will search for terrestrial planets in the habitable zone of solar-type stars. Because of telemetry limitations, PLATO targets need to be pre-selected. We present an all sky catalog that will be fundamental to select the best PLATO fields and the most promising target stars, derive their fundamental parameters, analyze the instrumental performances, and then plan and optimize follow-up observations. This catalog also represents a valuable resource for the general definition of stellar samples optimized for the search of transiting planets.
Code Language(s): N/A
Last updated: Nov. 5, 2021
Version: 1.1
Subcategories:
Host Star Catalogs
SWAMPE is a Python package for modeling the dynamics of exoplanetary atmospheres. SWAMPE is an intermediate-complexity, two-dimensional shallow-water general circulation model. Benchmarked for synchronously rotating hot Jupiters and sub-Neptunes, the code is modular and could be easily modified to model dissimilar space objects, from Brown Dwarfs to terrestrial, potentially habitable exoplanets. SWAMPE can be easily run on a personal laptop.
Code Language(s): Python
Last updated: Jun. 6, 2023
Version: 1.0.0
Subcategories:
2D/3D Atm Models
Toy Coronagraph is a Python package designed to quantify the impact of exozodiacal dust on exoplanet detection. It takes circularly symmetric disk images and point spread functions, and exoplanet orbital parameters to generate key metrics like contrast curves, signal-to-noise ratios, and dynamic visualizations of exoplanet motion under the dust background. The package also provides tools for generating vortex coronagraph PSFs and includes example disk images. Toy Coronagraph empowers researchers to understand exozodiacal dust, develop mitigation strategies, and optimize future telescope designs and mission time, ultimately advancing the search for potentially habitable worlds.
Code Language(s): Python
Last updated: Apr. 8, 2025
Version: 1.6.1
Subcategories:
Data Visualization Tools
Direct Imaging Instr. Models
This code performs an MC sampling to estimate what fraction of rocky planets could harbor liquid water on their surfaces.
Published in "A Population-based Habitable Zone Perspective", 2015, The Astrophysical Journal, Volume 813, Issue 1, article id. 9, 11 pp.
 icon in a resource box to provide suggestions for an individual tool or tools.
icon in a resource box to provide suggestions for an individual tool or tools.